Endpoint
DNS Name / IP Address | Name of the controller in the Domain Name System (DNS) where the OPC UA server is installed as embedded application. A name server can uniquely identify the server using this name by mapping the DNS name to the controller's IP address. |
| Information Model | Specifies the implementation of the information model and therefore the visibility of data for OPC UA clients.Using these options, you can define the data structure the OPC UA server will provide to its clients.'IN/OUT-Port visibility'
- 'all': all ports and variables contained in the application's GDS (Global Data Space) are visible and accessible for OPC UA clients.
- 'marked': only ports and variables for which the 'OPC' property is selected in the variables declaration table are visible and accessible for OPC UA clients. Using this option and selecting the required variables in the declaration table, the load of the OPC UA server as well as the communication traffic can be reduced.
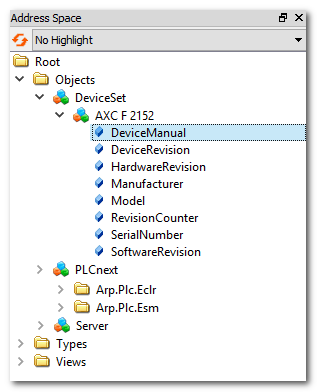
- 'none': clients cannot subscribe any port or variable via the OPC UA server. The entire 'PLCnext' node is excluded from the data information model.The Device Information (DI, according to the OPC UA standard) remains visible for clients. This includes controller information such as hardware and software revision numbers, serial number, manufacturer name, model specification, etc.
 Example Example
Information model visible in an example client. The OPC UA server is embedded in the PLCnext Technology controller AXC F 2152. The setting 'all' results in the following data structure:
- The 'PLCnext' node contains the ports and variables provided for the OPC UA clients.
- The 'AXC F 2152' node contains the OPC UA standard Device Information
|
Subscription Settings
Subscription Kind | Kind of PLCnext subscription that is used by the OPC UA server.Possible values:
- 'Direct Read': With this setting, values are recorded independently of the ESM tasks defined in your controller application. Instead, values are read directly from the respective variables as soon as the responsible firmware function is called. This way, data subscriptions from different ESM task cycles are possible.
This setting may be useful for the asynchronous subscription of non-time-critical data. It has no influence on the real-time behavior.
'Direct Read' is the default setting for new projects and after the replacement of an older controller by a controller with firmware version 2021.0 LTS or newer.
- 'High Performance': In this mode, simultaneous reading and writing of data is possible. Each access takes place ESM-task-synchronoulsy. This subscription type consumes the least memory. It actually has impact on the real-time behaviour but less than the 'Real Time' mode.
This mode is suitable for the most data acquisition scenarios.
- 'Real Time': In this mode, simultaneous reading and writing of data is made with minimum access times. Therefore, it enables the fastest data access of all three modes but requires the most memory. Subscription is made task-synchronously.
This mode is suitable for subscribing variables in very fast tasks. However, it influences the real-time behavior even more than in 'High Performance' mode.
|
 Example
Example
