CPU Load Measurements (SPLC 3000 class)
This help topic describes the effect of the SF_RecipeWrite function block in a safety application on the CPU load of a SPLC 3000 class Safety PLC.
Underlying measurement scenario:
The Safety PLC was operated with a cycle time of 10,000 µs (default setting is 5,000 µs).
The CPU load was measured sequentially for 0 to 1024 instances of the block. With 0 instances the safety application consists of an empty program POU S_Main.
With the number of FB instances, the number of recipe files was increased accordingly from 0 to the maximum number of 8, so that all data sets were always processed in each file.
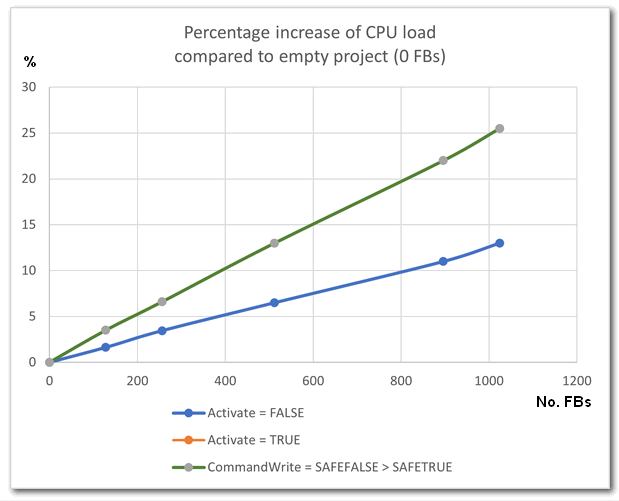
In the measurement protocol shown below, the CPU utilization is indicated when the FBs are deactivated (Activate = FALSE) as well as when the FBs are activated (Activate = TRUE) and when a write request is made (i.e. after a rising edge at CommandWrite).
The measurement results in the table show the percentage change in CPU load (i.e. the delta) compared to "idle", i.e., with zero FB instances in the safety program.
| No. of FBs (each data set used) | Increases of the CPU load in % (compared to zero FBs in the program) with FBs... | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| deactivated | activated/writing data | ||
| 128 | 2 | 4 | |
| 256 | 3 | 7 | |
| 512 | 7 | 13 | |
| 896 | 11 | 22 | |
| 1024 | 13 | 26 | |
The CPU load values are identical when the FBs are activated and if they are writing. Therefore the curves overlap in the following diagram:
| Further Info
Refer to the topic "CPU load optimization for a pair of instances for writing and reading of a recipe file". |