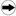SF_Guard
Help version 2.0 / Issue date: 2024.04
The following description is valid for the function block SF_GuardOut_V2_0z, Version 2.0z (where z = 0 to 9).
|
Short Description
| The safety-related SF_Guard function block monitors a guard (e.g., door) with according to the DIN EN ISO 14120 standard.S_StartReset can be used to specify a start-up inhibit and S_AutoReset can be used to specify a restart inhibit. |
|
Block Icon
|  |
|
Inputs
|  Activate Activate
| Short description | Value |
State-controlled input for activating the function block. Data type: BOOL
Initial value: FALSE |
-
FALSE: Function block inactive.
-
TRUE: Function block activated.
|
Refer to the topic "Activate" for details.
 S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2
| Short description | Value |
State-controlled inputs for the connected position switches of the door. For the S_GuardOut output to switch to SAFETRUE, both inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 must switch to SAFETRUE within the time set at DiscrepancyTime. Data type: SAFEBOOL
Initial value: SAFEFALSE
Hinweis
If only one signal reports the status of the door (one position switch only), this must be connected in parallel to both inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2. Where this is the case, a time of 0 seconds must be set at DiscrepancyTime. |
|
-
SAFEFALSE: Position switch reports open state
-
SAFETRUE: Position switch reports closed state
|
Refer to the topic "S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2" for details.
 DiscrepancyTime DiscrepancyTime
| Short description | Value |
Input for specifying the maximum permissible discrepancy time for the closing operation of the safety equipment.Data type: TIME
Initial value: #0msIf S_GuardSwitch1 or S_GuardSwitch2 switches to SAFETRUE, the respective other input (S_GuardSwitch1 or S_GuardSwitch2) must also switch to SAFETRUE within the time set at DiscrepancyTime for the switching operation to be considered as valid.
If not both inputs have switched to SAFETRUE after the time set at DiscrepancyTime has elapsed, an error message is generated (Error = TRUE) and the S_GuardOut output remains in the defined safe state SAFEFALSE. | Enter a time value according to your risk analysis. |
Non-conformance to safety function requirements
- Verify that the time value set at DiscrepancyTime corresponds to your risk analysis.
- Be sure that your risk analysis includes an evaluation for incorrectly setting the time value at the DiscrepancyTime parameter.
- Validate the overall safety-related function with regard to the set DiscrepancyTime value and thoroughly test the application.
|
Refer to the topic "DiscrepancyTime" for details.
 S_StartReset S_StartReset
| Short description | Value |
State-controlled input for specifying the
start-up inhibit after the Sicherheitssteuerung has been started up or the function block has been activated.An active
start-up inhibit must be removed manually by means of a positive signal edge at the Reset input. A deactivated
start-up inhibit causes the S_GuardOut output to switch to SAFETRUE automatically when the function block is activated and the safety-related function is not requested.Data type: SAFEBOOL
Initial value: SAFEFALSE |
-
SAFEFALSE: With
start-up inhibit
-
SAFETRUE: Without
start-up inhibit
|
Non-conformance to safety function requirements
- Verify the impact of a deactivated start-up inhibit (S_StartReset = SAFETRUE) and/or restart inhibit (S_AutoReset = SAFETRUE) on your machine or process prior to implementation.
- Observe the regulations given by relevant sector standards regarding the start-up/restart inhibit.
- Verify that a suitable start-up inhibit is in place at another location or using other means.
|
Refer to the topic "S_StartReset" for details.
 S_AutoReset S_AutoReset
| Short description | Value |
State-controlled input for specifying the restart inhibit after the previously opened safety equipment has been closed (in other words, after the SAFETRUE signal has returned at inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2).Data type: SAFEBOOL
Initial value: SAFEFALSEAn active restart inhibit must be removed manually by a positive signal edge at the Reset input. A deactivated restart inhibit causes the S_GuardOut output to switch to SAFETRUE automatically when the function block is activated and the safety-related function is no longer requested. |
-
SAFEFALSE: With restart inhibit
-
SAFETRUE: Without restart inhibit
|
Non-conformance to safety function requirements
- Verify the impact of a deactivated start-up inhibit (S_StartReset = SAFETRUE) and/or restart inhibit (S_AutoReset = SAFETRUE) on your machine or process prior to implementation.
- Observe the regulations given by relevant sector standards regarding the start-up/restart inhibit.
- Verify that a suitable start-up inhibit is in place at another location or using other means.
|
Refer to the topic "S_AutoReset" for details.
 Reset Reset
| Short description | Value |
Edge-triggered input for the reset signal:
- Resetting error messages when the cause of the error is no longer present.
- Manual resetting of an active start-up/restart inhibit (depending on which type(s) of inhibit the function block provides).
Data type: BOOL
Initial value: FALSE |
-
FALSE: Reset is not requested
- Edge FALSE > TRUE: Reset is requested
|
Hinweis
Resetting does not occur with a negative (falling) edge, as specified by standard EN ISO 13849-1, but with a positive (rising) edge.
To implement the reset with a falling edge (with regard to the mandatory acceptance procedure), use the function block SF_Reset. |
Resetting the function block by means of a positive signal edge at the Reset input can cause the S_GuardOut output to switch to SAFETRUE immediately (depending on the status of the other inputs).
Unintended start-up
- Include in your risk analysis the impact of the reset by means of a positive signal edge at the Reset input.
- Make certain that appropriate procedures and measures (according to applicable sector standards) have been established to help avoid hazardous situations when resetting.
- Do not enter the zone of operation when resetting.
- Ensure that no other persons can access the zone of operation when resetting.
- Use appropriate safety interlocks where personnel and/or equipment hazards exist.
|
Refer to the topic "Reset" for details.
|
|
Outputs
|  Ready Ready
| Short description | Value |
| Output for signaling "Function block activated/not activated".Data type: BOOL |
-
FALSE: Function block is not activated (Activate = FALSE) and all outputs of the function block are switched to FALSE/SAFEFALSE.
-
TRUE: Function block is activated (Activate = TRUE) and the output parameters represent the state of the safety-related function.
|
Refer to the topic "Ready" for details.
 S_GuardOut S_GuardOut
| Short description | Value |
| Output for enable signal of the function block.Data type: SAFEBOOL |
-
SAFEFALSE:
- The guard is not closed (S_GuardSwitch1 and/or S_GuardSwitch2 = SAFEFALSE)
-
or the function block is not activated
-
or the start-up/restart inhibit is active
-
or an error message is present.
-
SAFETRUE:
- Guard closed (S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 = SAFETRUE)
-
and the function block is activated
-
and the start-up/restart inhibit is not active
-
and no error message is present.
|
Refer to the topic "S_GuardOut" for details.
 SafetyDemand SafetyDemand
| Short description | Value |
Output for signaling "safety-related function requested".
This output displays whether the safety chain is interrupted and as a result, the attention of the operator is required. Data type: BOOL |
-
FALSE: Safety-related function is not requested.
-
TRUE: The safety-related function is requested.
|
Refer to the topic "SafetyDemand" for details.
 ResetRequest ResetRequest
| Short description | Value |
Output for signaling "reset is required".
This output indicates whether a reset by the operator is required. Data type: BOOL |
-
FALSE: No reset required.
-
TRUE: A reset is required:
- to remove an active start-up or restart inhibit (if available for this function block)
-
or to reset an error.
|
Refer to the topic "ResetRequest" for details.
 Error Error
| Short description | Value |
| Output for error message.Data type: BOOL |
-
FALSE: No error is present (that is to say, the FB is not in an error state) or the FB is not active.
-
TRUE: The function block has detected an error. The error state is shown at the DiagCode output.
|
Refer to the topic "Error" for details.
 DiagCode DiagCode
| Short description | Value |
| Output for diagnostic message.Data type: WORD | Diagnostic message of the function block.
The possible values are listed and described in the topic "Diagnostic codes". |
Refer to the topic "DiagCode" for details.
|
| Detailed information |  Signal sequence diagram Signal sequence diagram
This diagram is based on typical monitoring of a guard with , where both position switches connected to inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 switch within the time set at DiscrepancyTime.
Additional assumptions:
S_StartReset = SAFEFALSE: Start-up inhibit after the function block has been activated and the Sicherheitssteuerung has started up
S_AutoReset = SAFEFALSE: Restart inhibit after the previously opened safety equipment has been closed (i.e., after the SAFETRUE signals have returned at inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2).
| 0 | The function block is not yet activated (Activate = FALSE). As a result, all outputs are FALSE or SAFEFALSE. |
| 1 | Both inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 are SAFETRUE. However, the S_GuardOut output is still SAFEFALSE, since a start-up inhibit is specified after the Sicherheitssteuerung has been started up by S_StartReset = SAFEFALSE. |
| 2 | A positive edge at the Reset input resets the start-up inhibit and the S_GuardOut output switches to SAFETRUE. |
| 3 | The safety equipment is opened. S_GuardSwitch2 and S_GuardSwitch1 switch to SAFEFALSE one after the other, and the S_GuardOut output becomes SAFEFALSE. |
| 4 | The safety equipment is closed. Measurement of the discrepancy time begins with the switch from SAFEFALSE to SAFETRUE at S_GuardSwitch2. The second input S_GuardSwitch1 also switches to SAFETRUE during the time set at DiscrepancyTime. As a restart inhibit is specified by S_AutoReset = SAFEFALSE after the safety equipment has been closed (S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 = SAFETRUE), the S_GuardOut output only becomes SAFETRUE once the restart inhibit has been removed by a positive edge at the Reset input. |
| 5 | The safety equipment is opened. S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 switch to SAFEFALSE one after the other, and the S_GuardOut output becomes SAFEFALSE. |
| 6 | The safety equipment is closed. Both inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 become SAFETRUE at the same time. The function block detects the permanent TRUE signal at the Reset input as an error. Output Error becomes TRUE and output S_GuardOut remains SAFEFALSE. |
| 7 | The Reset input becomes FALSE; this causes the error message to be reset. |
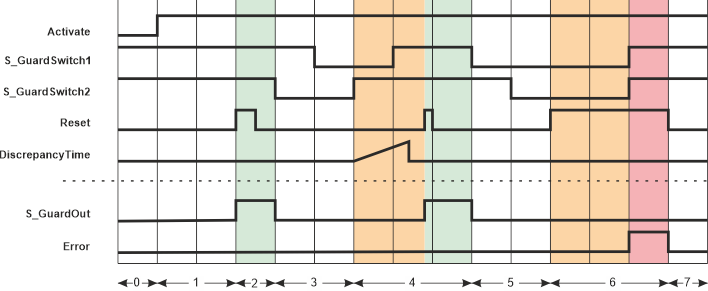
 Application example: Door monitoring using a mechanical position switch, start-up inhibits activated Application example: Door monitoring using a mechanical position switch, start-up inhibits activated
This example describes how a mechanically activated position switch with 2 N/C contacts is evaluated using the safety-related SF_Guard function block. Position switch B1 is connected to input terminals 1.1 and 2.1 of safety-related input device PSDI 1.
The signals from position switch B1 are evaluated, based on two channels, for equivalence in the safety-related input device, which has been parameterized accordingly. The resulting signal is assigned to the global I/O variable B1_GMControl_In. This variable is connected to the inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2 of the safety-related SF_Guard function block for evaluation.
B1_GMControl_In is SAFETRUE if both inputs of the safety-related input device PSDI 1 are SAFETRUE at the same time (safety equipment closed) and the safety-related input device PSDI 1 does not report any errors as regards exceeding the time set at DiscrepancyTime.
Hinweis
Since only one signal reports the status of the door in this example (one position switch), this is connected in parallel to both inputs S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2. In this case, a value of 0 seconds is set at input DiscrepancyTime. |
The function block is perpetually activated by a TRUE constant at the Activate input.
S_StartReset = SAFEFALSE specifies a start-up inhibit after the Sicherheitssteuerung has been started up or the function block has been activated. Furthermore, S_AutoReset = SAFEFALSE specifies a restart inhibit for the function block after the door has been closed. Both inhibits are only removed when there is a positive signal edge at the Reset input.
To this end, the S1 reset button is connected to input terminal 1.1 of the standard input device DI 1. The terminal is assigned to the global I/O variable S1_Reset_GM, which in turn is connected to the function block input Reset.
Hinweis
The enable signal at the S_GuardOut output of the SF_Guard function block is connected to additional safety-related function blocks or functions and controls the application accordingly. |
| S1 | Reset |
| B1 | Door switch with two positively driven N/C contacts for positive opening operation  (SAFETRUE, if safety equipment closed). (SAFETRUE, if safety equipment closed). |
| (*1) | Door: open |
| (*2) | Door: closed |
 | See note above the illustration. |
 Function block instantiation Function block instantiation
The IEC 61131-3 standard defines function block instantiation. Instantiation means, a function block is defined once and can be used (instantiated) several times. This applies to all standard and safety-related FBs (local POUs as well as firmware and user library FBs).
Why instantiation?
A function block has an internal memory where it stores its own processing data (local variables). As a consequence, the output values calculated by the FB depend on the internally stored values. The same input values applied to an FB instance do not necessarily deliver the same results in another FB instance.
Therefore, it is necessary to store the internal data of the FB to a separated memory area each time the function block is processed, i.e., for each FB instance. To uniquely identify each FB instance and to clearly separate its memory area, instance names are used. The instance name of a function block has to be declared in the 'Variables' table of the POU where the FB is going to be used.
The following applies:
- Function blocks can be instantiated in other function blocks or in program POUs. Calling FBs in function POUs is not possible.
- Functions are called without instantiation because they do not have an internal memory.
Safety-related and standard (non-safety-related) code is strictly distinguished in PLCnext Engineer. If a Safety PLC is included in your project, the following applies:
- Safety-related FBs can only be instantiated in safety-related POUs but not in standard (non-safety-related) POUs.
- User-defined standard FBs can only be instantiated in standard POUs. They cannot be called in safety-related POUs.
- Particular standard firmware FBs can be instantiated in both safety-related and standard POUs.
Hinweis
When inserting a standard FB into a safety-related SNOLD network, the rules for implicit type conversion (safety-related to standard) apply. |
 Example for the instantiation of a safety-related PLCopen function block Example for the instantiation of a safety-related PLCopen function block
The safety-related PLCopen function block 'SF_EmergencyStop_V2_00' was inserted into the project via a library. It is then available in the 'Programming' category of the COMPONENTS area. There is a folder with the same name as the library that provides the FBs for insertion into the safety-related code.
The FB is to be called twice in the code of the safety-related program 'S_Main' to evaluate the status of two safety-related emergency stop command devices. For each FB instance, an instance name is declared in the 'Variables' table of the calling program: EStop_M1 and EStop_M2. The FB instances have been inserted into the code worksheet, each instance with different variables connected to its input and output formal parameters.
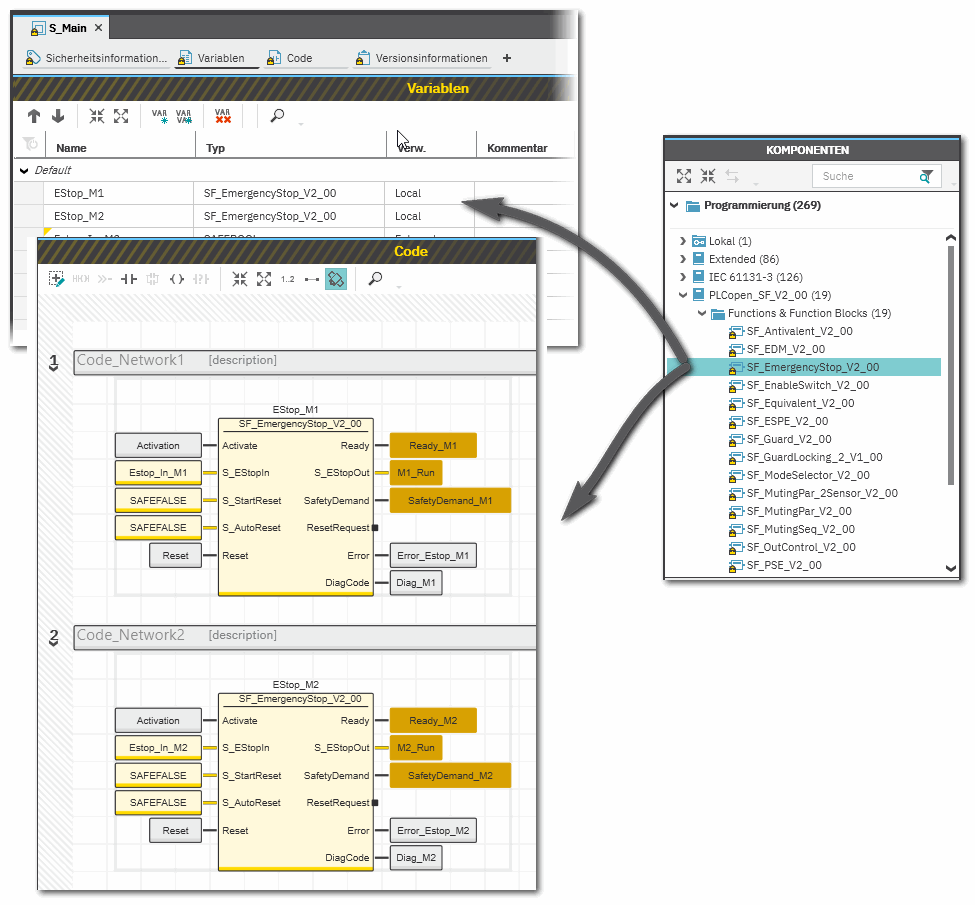
Additional information is available in the following sections:
|
 ‣ Verriegelungen gemäß DIN EN ISO 14119/14120
‣ Verriegelungen gemäß DIN EN ISO 14119/14120
 Activate
Activate
 S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2
S_GuardSwitch1 and S_GuardSwitch2
 DiscrepancyTime
DiscrepancyTime
 S_StartReset
S_StartReset
 S_AutoReset
S_AutoReset
 Reset
Reset
 Ready
Ready
 S_GuardOut
S_GuardOut
 SafetyDemand
SafetyDemand
 ResetRequest
ResetRequest
 Error
Error
 DiagCode
DiagCode
 Signal sequence diagram
Signal sequence diagram
 Application example: Door monitoring using a mechanical position switch, start-up inhibits activated
Application example: Door monitoring using a mechanical position switch, start-up inhibits activated
 Function block instantiation
Function block instantiation