|
Description
| The object-oriented MUTEX function block is used to manage the access to shared resources across multiple tasks. It is used to make access to these shared resources mutually exclusive. The FB prevents race conditions, data corruption, or unexpected behavior when multiple tasks try to access shared resources at the same time.
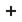 How a Mutex works How a Mutex works
A mutex acts as a locking mechanism for tasks that use shared data. A mutex has a locked and an unlocked status. When a task wants to access shared data, it must first acquire the mutex. If the mutex is not locked by any other task, the task locks the mutex and continues executing. If the mutex is already locked by another task, the requesting task waits for the mutex to be unlocked. The task will be blocked until the mutex is released. Tasks that are in the waiting state are added to the mutex queue. After completing the operation on the shared data, the task releases the mutex (unlocks it), allowing other tasks to acquire it and access the shared data.
Note
In case of a mutex lock, a task watchdog can occur. It is therefore recommended to use a TRYLOCK method instead of a LOCK method. |
The function block provides the following methods that are used for interacting with a mutex:
- LOCKLocks the mutex (becomes the owner of the mutex). If the mutex is already locked by another task, the task will wait (block) until it's available (unlocked by another task).
Note
In case of a mutex lock, a task watchdog can occur. It is therefore recommended to use a TRYLOCK method instead of a LOCK method. |
- UNLOCKUnlocks the mutex, allowing the next waiting task to become the owner of the mutex (to lock the mutex).Must always be called after a successful TRYLOCK or LOCK (return value TRUE).
Note
Only the task that locked the mutex is able to unlock it. |
- TRYLOCKTries to lock the mutex (to become the owner of the mutex). It checks if the mutex is available:
- If yes - it locks the mutex and returns TRUE.
- If no - it returns FALSE immediately, without waiting.
- IS_ENTEREDChecks whether the current task holds the lock on the specified mutex.
- TRUE = Task has locked the mutex
- FALSE = Task has not locked the mutex.
|
 How a Mutex works
The function block provides the following methods that are used for interacting with a mutex:
How a Mutex works
The function block provides the following methods that are used for interacting with a mutex: