NAT
The 'NAT' view shows the NAT (Network Address Translation) topology. NAT is a protocol that is used to link one network to another network. It translates IP addresses of devices on one network (called the inside network) into a single IP address on another network (outside network). The address translation is done by the NAT router (router with enabled NAT). It maps the IP addresses of the devices on the inside network (called NAT clients) to a single, unique IP address. This unique IP address is then used to communicate with the devices on the outside network. In industrial networks, for example, NAT is used to link different subnets to each other whereby identical IP addresses are used within all subnets.
The NAT router is represented in the physical topology by a specific symbol (see below). If you select a NAT client, the NAT router(s) which perform an address translation for the selected device are highlighted (all other NAT clients are greyed out). If you select a NAT router, all NAT clients for which the router performs an address translation are highlighted (NAT clients which are not affected by the address translation of the selected router are greyed out). The device tooltip shows, among others, which NAT operations are performed for the device (see the example below). Non-NAT clients are greyed out in the topology.
The name of a NAT client shows the IP address translated by the NAT router. This IP address is used for communication. The configured IP address of the device can be derived from the tooltip of the device (see the example below). The tooltip also provides information on the NAT operations performed for the device.
Symbols specific to the 'NAT' view
| Note
You can switch the display of the devices between two modes: standard and individual. In standard mode, the device symbol as listed in the following table are used for the representation of the devices. In individual mode, the device icon stored in the device description file of the device (e.g., FDCML, GSDML, etc.) is shown as device symbol. To switch the display, click the  button in the toolbar of the 'Physical Topology' editor (see also the section "Enable / disable display of device graphics" for further details). button in the toolbar of the 'Physical Topology' editor (see also the section "Enable / disable display of device graphics" for further details). |
| Symbol | Device |
|---|---|
 | NAT router |
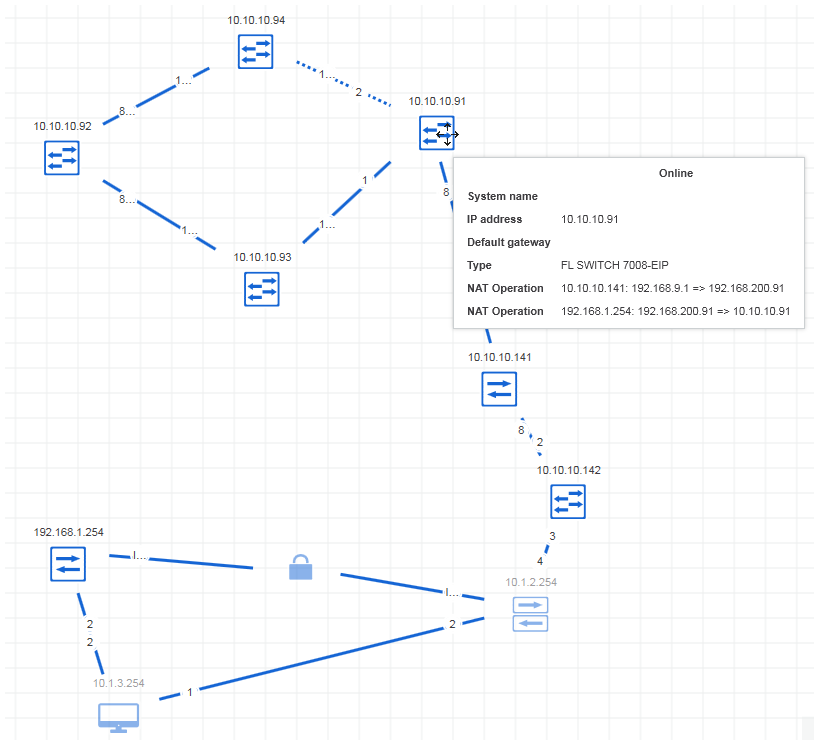
Example of a NAT topology
The example network contains two NAT routers (IP addresses 10.10.10.141 and 192.168.1.254) and five NAT clients. The tooltip of a NAT client shows the NAT operations performed for the device. For example, for the NAT client with the IP address 10.10.10.91 there are two NAT operations:
- NAT operation 1: 10.10.10.141: 192.168.9.1 => 192.168.200.91Meaning: The NAT router 10.10.10.141 translates the IP address 192.168.9.1 (this is the real IP address configured for the device) into the IP address 192.168.200.91.
- NAT operation 2: 192.168.1.254: 192.168.200.91 => 10.10.10.91Meaning: The NAT router 192.168.1.254 translates the IP address 192.168.200.91 into the IP address 10.10.10.91. This is the IP address which is used for the communication.