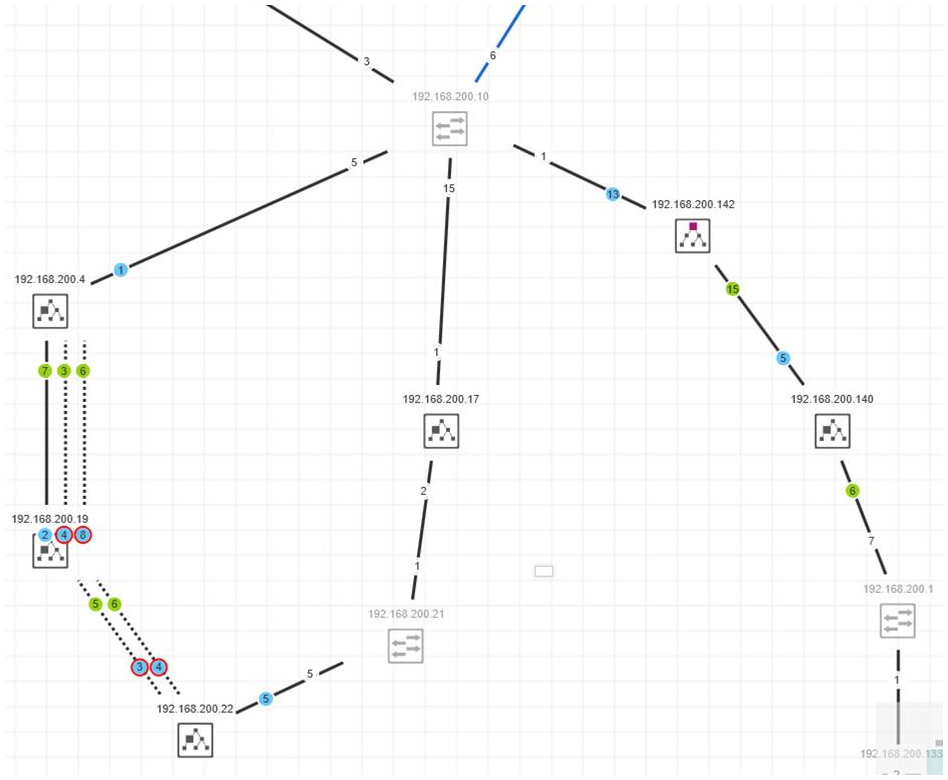
Redundancy (R)STP
The 'Redundancy (R)STP' view shows the spanning tree topology. Devices running the (Rapid) Spanning Tree Protocol ((R)STP) are represented in the physical topology by specific symbols (see below). PLCnext Engineer detects, for example, which device is the root bridge and which devices are non-root bridges. The role of a port (root port, designated port, alternate port) is represented by a specific port symbol. The port state and also the port role are shown in the port tooltip. Non-(R)STP devices are greyed out in the topology.
Symbols and ports specific to the 'Redundancy R(STP)' view
Note
You can switch the display of the devices between two modes: standard and individual. In standard mode, the device symbol as listed in the following table are used for the representation of the devices. In individual mode, the device icon stored in the device description file of the device (e.g., FDCML, GSDML, etc.) is shown as device symbol. To switch the display, click the  button in the toolbar of the 'Physical Topology' editor (see also the section "Enable / disable display of device graphics" for further details). button in the toolbar of the 'Physical Topology' editor (see also the section "Enable / disable display of device graphics" for further details). |
| Symbol | Device / Port |
 | (R)STP root bridgeThe (R)STP root bridge is the bridge with the lowest numerical bridge ID in the (R)STP network. It functions as the root in the spanning tree. There is only one root bridge in the (R)STP network. All other (R)STP bridges in the network are non-root bridges.The device tooltip shows, among other things, the root bridge ID. |
 | (R)STP bridgeThe (R)STP bridge exchanges data frames with the root bridge via the root port. It creates Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) only when it receives a configuration BPDU from the root bridge.The device tooltip shows, among other things, the bridge ID. |
 | Designated portThe designated port is the port that is used to access a LAN segment. It forwards data to the (R)STP root bridge from the LAN segment. The port tooltip shows the port role and the port state. |
 | Root portThe root port is the port that provides the lowest cost path from the non-root bridge to the root bridge. It forwards the data to the root bridge. The port tooltip shows the port role and the port state. |
 | Alternate portThe alternate port is the port that becomes the root port if the primary root port fails. The port tooltip shows the port role and the port state. |
Example of a (R)STP topology
 button in the toolbar of the 'Physical Topology' editor (see also the section "Enable / disable display of device graphics" for further details).
button in the toolbar of the 'Physical Topology' editor (see also the section "Enable / disable display of device graphics" for further details).