Role Mapping in the GDS Port List: Assigning PLCnext Ports
This topic contains the following sections:
The
GDS Port List of the 'PLCnext' PLANT node contains all ports which are available in the project (defined in a local program POU or contained in an included externally developed program). The
GDS Port List of program instance nodes in the PLANT contains the ports relating to the respective instance.
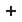 Example for a program instance with instance-related I/O variables and PLCnext ports
Example for a program instance with instance-related I/O variables and PLCnext ports
In the following figure, the 'MyProg1' program instance has been double-clicked in the PLANT.
The program instance contains both:
- The GDS Port List is available because ports are declared in the program type ('Usage' set to 'IN Port' or 'OUT Port').
- The Data List is available because the program type contains program-global variables ('Usage' = 'Program') for which a data direction 'I/Q' has been selected. Such variables become instance-related I/O variables which can be assigned to process data items.
Ports are either declared in a local program POU with one of the keywords 'IN Port' or 'OUT Port' or they are part of and handed over from instantiated external programs. IN and OUT ports can be assigned (mapped) to each other. This way, data can be transferred between programs developed in the
current project and externally developed programs (for example using C++) which are instantiated in a task.
 Background: Ports of PLCnext Technology controllers
Background: Ports of PLCnext Technology controllers
For controllers of the PLCnext Technology generation, input and output ports can be used in addition to or instead of resource-global variables. Programs communicate using ports, i.e., data can be read from and written to programs via ports.
Via ports, communication is even possible between IEC 61131-3-compliant programs and programs developed with a non-IEC 61131-3 programming language such as C++.
For that purpose, input and output ports can be assigned to each other using the role mapping function in the GDS Port List. Port Lists are available on the 'PLCnext' PLANT node and on program instance nodes. A Port List contains the ports which are relevant for the respective PLANT node.
All port connections are stored in the Global Data Space of the PLCnext Technology controller.
How to assign ports
The mapping of ports in a
GDS Port List is done by simply selecting an entry in the corresponding columns using the Role Picker as follows:
Note
In Data Lists, Port Lists and variables tables, the selection in drop-down lists is done with a single-click, not with a double-click. |
- In the table, left-click into the field where you want to assign a data item and which is showing the text 'Select ... here' or move the table cursor using the arrow keys or <Tab>/<Shift>+<Tab> to this table field and press <Enter>.The Role Picker appears. It is divided into a tree on the left and data items on the right. The Role Picker only provides data items for selection which match the data type for the assignment to be done.
- Select a folder in the tree on the left and then the data item on the right by clicking it or pressing the <Enter> key.
Note
The Role Picker retains your last selection as long as the editor has not been closed. |
Use the following keys to navigate in the Role Picker:
| Press the shortcut ... | ... to ... |
| <Tab>/<Shift> + <Tab> | switch between the folders on the left and the entries on the right. |
| <ArrowDown>/<ArrowUp> | move the cursor down/up. |
<Enter>
(focus on the right side) | select the currently marked entry, close the selection control and apply the entry to the table field. |
<ArrowRight>/<ArrowLeft>
(focus on the left side) | expand/collapse the currently marked folder on the left. |
Note
Ports may be of complex data types, such as arrays or structs. In this case, the Role Picker in the
GDS Port List supports the selection of individual port members.
After disconnecting a port member, it remains unconnected in the
GDS Port List. It can then be deleted with the toolbar command 'Delete unconnected port member'. See topic "Ports of user-defined data types" for details. |
1-to-n assignment for output ports
Output ports can be read several times in an application. The
GDS Port List allows to assign an output port to several input ports (1-to-n assignment). For that purpose, the output port has to be duplicated. Duplicating is only possible for already assigned output ports.
Proceed as follows to assign an output port to several input ports in the
GDS Port List:
- Assign the desired output port to an input using the Role Picker as described above.
- Duplicate the output port by selecting its table row and choosing 'Duplicate Output Port' from its context menu or clicking the corresponding button on the Data List toolbar:

- Assign the duplicated output port to the desired input port.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 if desired: create and assign another copy of the output port.
Removing 1-to-n assignment and deleting duplicated output ports
- Delete an assignment between a duplicated output port by selecting the context menu command 'Disconnect IN Port' or selecting the respective button on the Data List toolbar:
- Delete the duplicated output port which is no longer assigned now:

- Repeat steps 1 and 2 for each duplicated port to be deleted.
Rules for assigning ports
The following rules apply when mapping ports in the GDS Port List.
 Use case 1: Both data types to be assigned are elementary data types...
Use case 1: Both data types to be assigned are elementary data types...
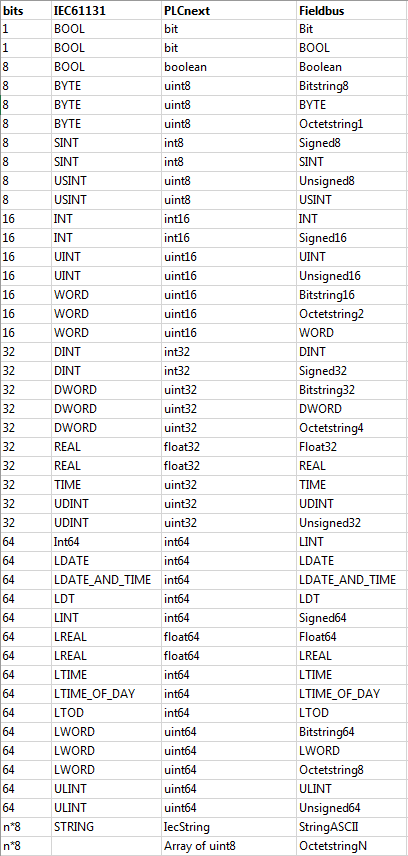
- If both data types are from the PLCnext/C++ domain, the following assignments are possible:
- If at least one type is from a non-PLCnext/C++ domain, the types have first to be mapped according to the table "Data type mapping table: IEC 61131 - PLCnext - Fieldbus" below. Afterwards, they can be assigned as shown in the previous item.
- If at least one type is from Fdcml domain and is mapped to an array in the PLCnext/C++ domain (like BitstringX), the assignment is possible as described in "Use case 2".
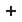 Use case 2: both data types to be assigned are arrays...
Use case 2: both data types to be assigned are arrays...
Precondition: assignment is only possible if the element counts are equal.
- If the array base types are elementary, the following is distinguished:If both base types are from the PLCnext/C++ domain, the assignment is possible if the base types match exactly.If at least one base type is from a non PLCnext/C++ domain, the base types have to mapped to the PLCnext/C++ domain according to the table "Data type mapping table: IEC 61131 - PLCnext - Fieldbus" below. Afterwards, an assignment is possible if the mapped base types match exactly.
- If the array base types are structures, assignment is possible according as described in the following section "Use case 3".
 Use case 3: both data types are structures
Use case 3: both data types are structures
Precondition: assignment is only possible if the structure field count and field names match (ignore case).
- If both field types are elementaries from the PLCnext/C++ domain, assignment is possible if the types match exactly.
- If both field types are elementaries and at least one field type is from a non PLCnext/C++ domain, first the field types have to be mapped according to the table "Data type mapping table: IEC 61131 - PLCnext - Fieldbus" below. Afterwards, an assignment is possible if the mapped types match exactly.
- If both field types are arrays, an assignment is possible according to "Use case 2".
- If both field types are structures, an assignment is possible according to the current "Use case 3" list.
- If both field types are enumerations, an assignment is possible according to "Use case 4".
 Use case 4: both data types are enumerations
Use case 4: both data types are enumerations
- If both base data types are from the PLCnext/C++ domain, assignment is possible if the base types match exactly.
- If at least one base type is from a non PLCnext/C++ domain, first the base types have to be mapped according to the table "Data type mapping table: IEC 61131 - PLCnext - Fieldbus" below. Afterwards, an assignment is possible if the mapped types match exactly.
 Use case 5: both data types are user defined strings like STRING(20), StaticString20, WSTRING(20), StaticWString(20)
Use case 5: both data types are user defined strings like STRING(20), StaticString20, WSTRING(20), StaticWString(20)
- Assignment is possible if the string capacities are equal.
- Wide strings can only be assigned to wide strings, non-wide strings can only be assigned to non-wide strings.
 Use case 6: one data type is an array and one data type is an elementary of type OctetString[n] or Bitstring[n]
Use case 6: one data type is an array and one data type is an elementary of type OctetString[n] or Bitstring[n]
The assignment of arrays to (process datum) ports with elementaries of the datatype OctetString[n] or BitString[n] is possible if the overall data size matches.
Note
Only possible for PLCnext controllers with firmware 2021.6 or higher. |
 Use case 7: special handling of safe FDCML datatypes (i.e., safe process datum)
Use case 7: special handling of safe FDCML datatypes (i.e., safe process datum)
The assignment of elementaries with safe FDCML datatypes is only possible when the data lengths are equal.
 Data type mapping table: IEC 61131 - PLCnext - Fieldbus
Data type mapping table: IEC 61131 - PLCnext - Fieldbus
 Example for a program instance with instance-related I/O variables and PLCnext ports
Example for a program instance with instance-related I/O variables and PLCnext ports
 Background: Ports of PLCnext Technology controllers
Background: Ports of PLCnext Technology controllers



 Use case 1: Both data types to be assigned are elementary data types...
Use case 1: Both data types to be assigned are elementary data types...
 Use case 2: both data types to be assigned are arrays...
Use case 2: both data types to be assigned are arrays...
 Use case 3: both data types are structures
Use case 3: both data types are structures
 Use case 4: both data types are enumerations
Use case 4: both data types are enumerations
 Use case 7: special handling of safe FDCML datatypes (i.e., safe process datum)
Use case 7: special handling of safe FDCML datatypes (i.e., safe process datum)